Chapter 18: Introduction to the Neural Network#
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the way machines learn from data, enabling them to perform tasks that once seemed impossible. From powering voice assistants to enabling autonomous vehicles, AI systems are now integrated into many aspects of daily life. At the core of this transformation are neural networks—computational models inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. These networks consist of interconnected nodes, or “neurons,” that process information in layers, allowing them to recognize patterns, make decisions, and improve over time. From early single-layer perceptrons to today’s deep architectures, neural networks have become a cornerstone of modern AI, powering breakthroughs in fields like healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems.
Neural networks are a type of supervised learning algorithm capable of identifying intricate patterns and relationships within data, making them suitable for tackling problems that traditional models often struggle with.
Although neural network algorithms have existed for many years, recent advancements in their architectures have led to significant improvements in performance on large-scale machine learning tasks. These developments form the foundation of what is now referred to as the “deep learning” methodology.
Deep learning, a branch of machine learning and artificial intelligence, leverages neural networks with multiple hidden layers to address highly complex tasks. These tasks range from natural language processing—such as speech recognition and text interpretation—to computer vision applications like object detection and image classification. The rise of deep learning over the past twenty years can be attributed to its remarkable effectiveness, the surge in computational power, and the growing accessibility of vast datasets.
Fundamentals of Neural Networks#
Neural networks are a powerful class of supervised learning algorithms capable of modeling complex, nonlinear relationships in data. Unlike traditional machine learning models, which rely on handcrafted features, neural networks automatically learn hierarchical representations from raw input. Key components include:
Input Layer: Receives raw data (e.g., pixels in an image, words in a text).
Hidden Layers: Intermediate layers that transform inputs through weighted connections and activation functions.
Output Layer: Produces the final prediction (e.g., class label, regression value).
Weights & Biases: Adjustable parameters learned during training.
Activation Functions: Introduce nonlinearity (e.g., ReLU, Sigmoid, Tanh).
Training a neural network involves forward propagation (passing data through the network) and **backpropagation **(adjusting weights based on error gradients using optimization techniques like gradient descent).
Neurons: The Building Blocks#
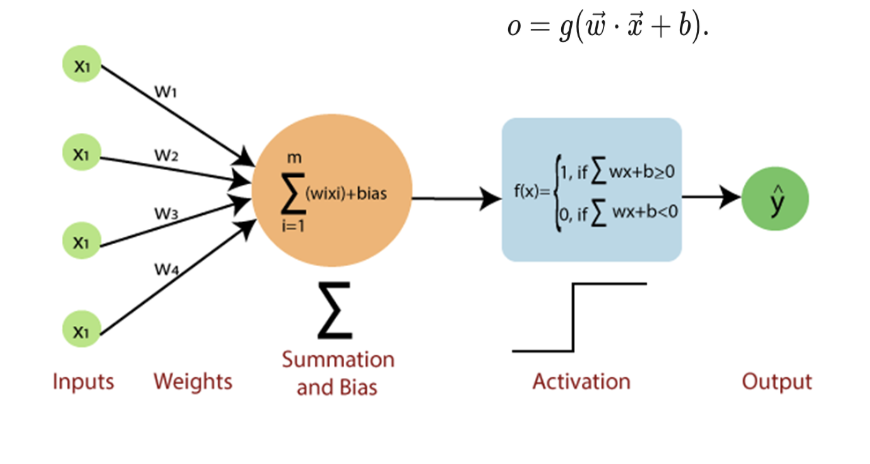
A neuron (or node) is the fundamental unit of a neural network, mimicking biological neurons. It receives inputs, processes them using weights and an activation function, and produces an output. Mathematically, a neuron’s operation can be represented as:
Where:
\(x_i\) = input features
\(w_i\) = weights
\(b\) = bias term
\(f\) = activation function
Weights and Biases#
Component |
Role |
|---|---|
Weights (( w_i )) |
Determine connection strength between neurons. They are adjusted during training to minimize prediction errors. |
Bias (( b )) |
Allows shifting the activation function to improve model flexibility. |