Law of Total Probability#
The Law of Total Probability allows us to compute the probability of an event based on a set of mutually exclusive and exhaustive scenarios.
If \(B_1, B_2, \dots, B_n\) are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events (they cover all possibilities), then for any event \(A\):
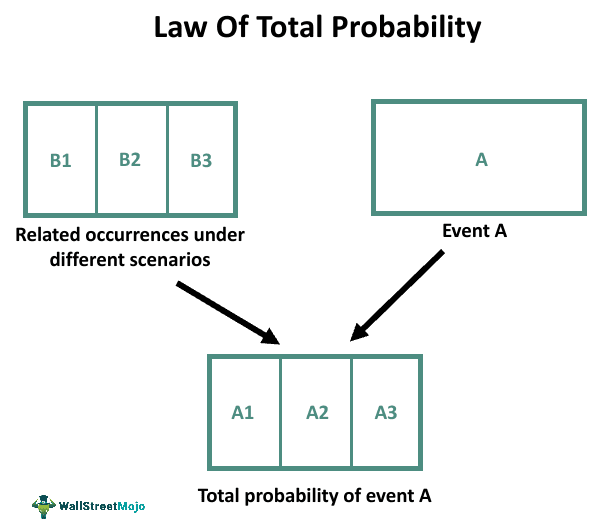
Figure: Law of Total Probability; illustrating how an event $A$ can occur under different scenarios $B_1, B_2, B_3$ and how their contributions combine to form the total probability of $A$. Source: WallStreetMojo
Explanation#
Mutually exclusive: No two \(B_i\) events happen at the same time.
Exhaustive: One of the \(B_i\) events must happen.
Conditional probability: \(P(A \mid B_i)\) is the probability of \(A\) given \(B_i\) occurs.
The law sums over all possible scenarios to get the total probability of \(A\).
Mutually exclusive and exhaustive event: Events that cannot happen at the same time (mutually exclusive) and cover all possible outcomes (exhaustive).
Example#
Suppose there are two factories producing light bulbs:
Factory 1 produces 60% of all bulbs, with a 1% defect rate.
Factory 2 produces 40% of all bulbs, with a 2% defect rate.
Question: What is the probability that a randomly chosen bulb is defective?
Solution using the Law of Total Probability:
So, there is a 1.4% chance that a randomly chosen bulb is defective.
### Python Code Example
# Probabilities
P_F1 = 0.6
P_F2 = 0.4
P_def_given_F1 = 0.01
P_def_given_F2 = 0.02
# Law of Total Probability
P_defective = P_def_given_F1 * P_F1 + P_def_given_F2 * P_F2
print("Probability of a defective bulb:", P_defective)
Probability of a defective bulb: 0.014