Putting It All Together: How Neural Network Training Happens#
After understanding how regularization helps prevent overfitting and improve generalization, it’s important to see how the entire training process operates in practice. Training a neural network involves repeatedly feeding data through the model in manageable portions, updating parameters, and gradually improving performance.
The next section explains the key concepts of batch size, iteration, and epoch, which organize how training data is processed and how the model learns over time.
Neural Network Training: Batch Size, Iteration, and Epoch#
When training a neural network, the dataset is usually too large to process all at once, so it is split into smaller parts called batches.
Batch Size#
The number of training examples used in one forward and backward pass.
For example, a batch size of 32 means the model processes 32 samples before updating weights.
Iteration#
One update of the model’s parameters (weights and biases).
Each iteration uses one batch of data.
Epoch#
One full pass over the entire training dataset.
If the dataset has 1000 samples and batch size is 100, then:
$\(
1 \text{ epoch} = \frac{1000}{100} = 10 \text{ iterations}
\)$
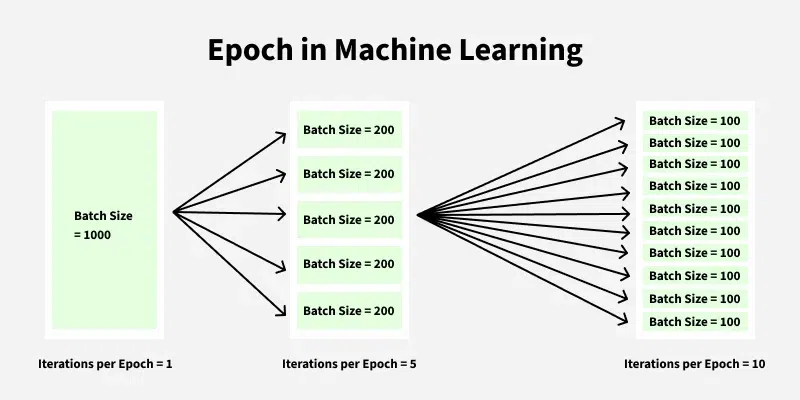
Figure: Epoch in Machine Learning
Training Process Overview#
Start Training: Initialize model parameters.
For each epoch (repeat multiple times):
Divide data into batches according to batch size.
For each batch:
Perform forward pass to calculate predictions.
Calculate loss based on predictions and true labels.
Perform backward pass (backpropagation) to compute gradients.
Update weights using gradients (e.g., gradient descent).
Repeat until model performance stabilizes or desired accuracy is reached.
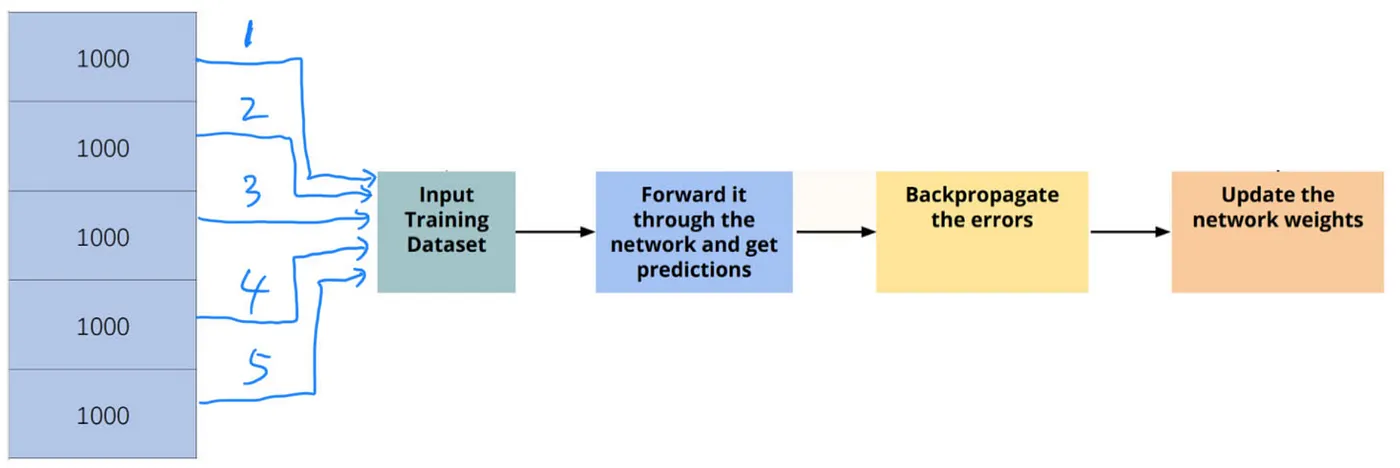
Figure: In the Input Training Dataset step, as different kinds of strategies, we can assign a Batch Size to determine how many training datasets are going to be used for one weights updating process. For example, there are 5000 images in total as the training datasets. If we set the Batch Size = 1000, we get 5 batches of training datasets. As a result, the weights updating process will be executed 5 times (Iterations).
Chapter Summary#
In this chapter, we explored the key components of training neural networks, including the forward and backward passes, how loss guides learning, and how weights are updated iteratively. We also discussed the role of batch size, iterations, and epochs in organizing the training process for efficient and effective learning.
Understanding these concepts lays the foundation for building, training, and optimizing deep learning models. In the next chapter, we will delve into advanced optimization techniques and strategies to further improve model performance.